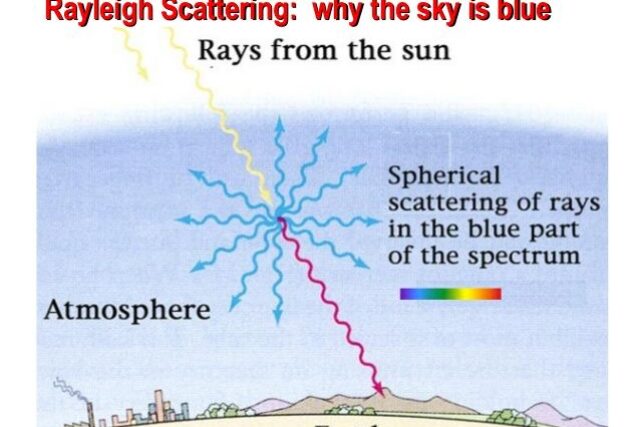
Why is the sky blue ? The sky is blue because of a process called Rayleigh scattering. This process occurs when white sunlight interacts with air molecules in the earth’s atmosphere. Air molecules are smaller than the wavelength of visible light, so they cause the light to scatter in all directions.
Blue light has a shorter wavelength than other colors, so it is more easily scattered by air molecules. Therefore, when we look at the sky, we see more blue light than any other color.
The process of Rayleigh scattering also explains why the sun appears red-orange at sunrise and sunset. When the sun rises and sets, sunlight has to travel a greater distance through the atmosphere to reach our eyes. On this journey, more blue light is scattered, so that the light that reaches our eyes is mostly red and orange light.
If there was no atmosphere, the sky would appear black, even during the day. This is because there are no air molecules to scatter sunlight. We can see this when looking at photos of the earth from space.
Here is a diagram showing how the Rayleigh scattering process occurs: